Stacks Blockchain API Overview
The Stacks blockchain API allows you to query the Stacks blockchain and interact with smart contracts. It was built to maintain paginated, materialized views of the Stacks Blockchain.
The Stacks Blockchain API is hosted by Hiro. Using it requires you to trust us as the hosted server, but in return we provide a faster development experience. If you want a fully trustless architecture for your app, you may wish to consider running your own API instance.
NOTE:
To explore the detailed documentation for the API endpoints, request and response formats, you can refer to the OpenAPI specification.
The source code for this project is available in our GitHub repository. You can explore the codebase, contribute, and raise issues or pull requests.
Architecture
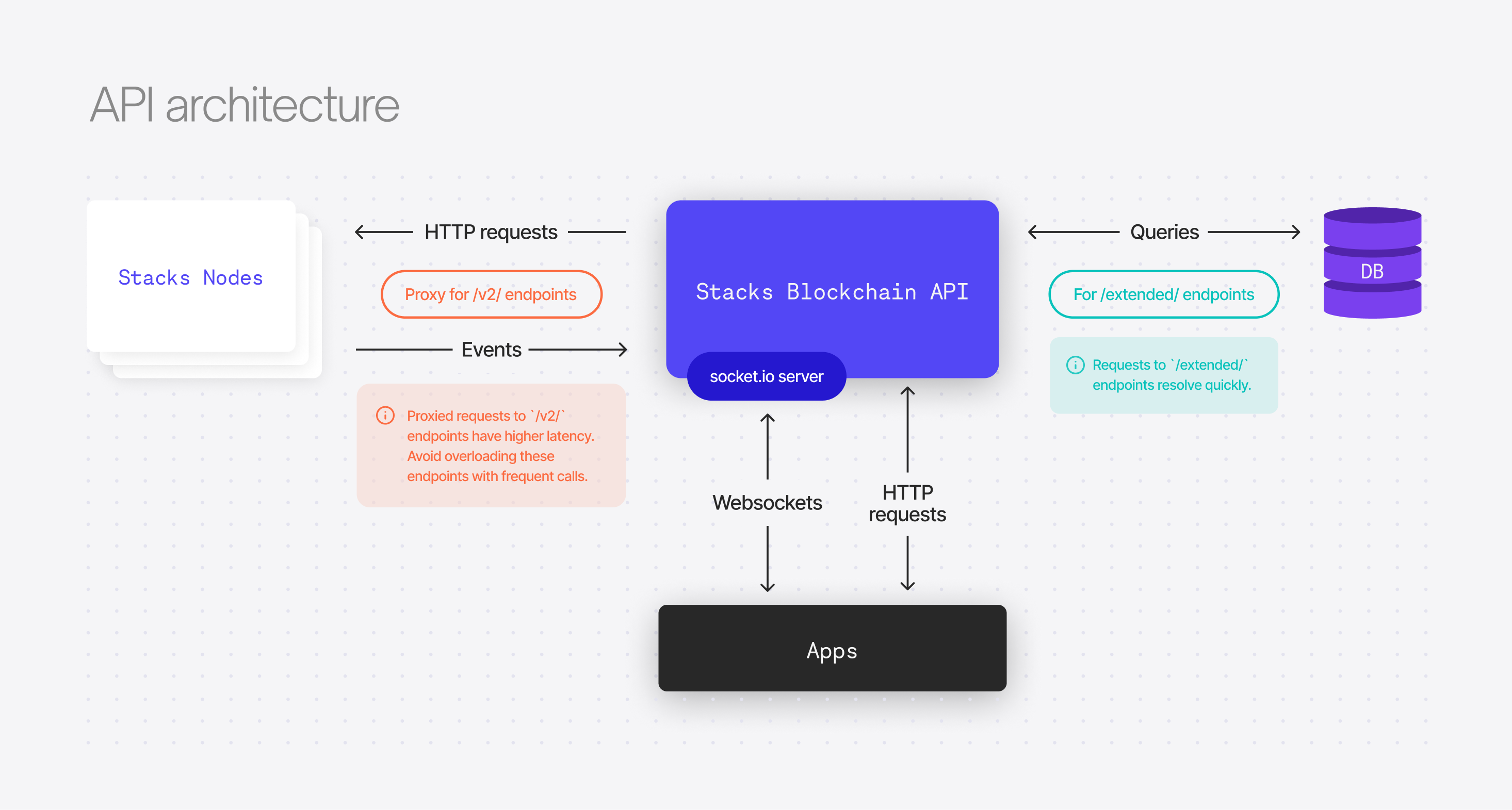
- The
stacks-nodehas its own minimal set of http endpoints referred to asRPC endpoints- The
stacks-blockchain-apiallows clients to access these endpoints by proxying them through to a load-balanced pool ofstacks-nodes. - See: https://github.com/blockstack/stacks-blockchain/blob/master/docs/rpc-endpoints.md -- some common ones:
POST /v2/transactions- broadcast a transaction.GET /v2/pox- get current PoX-relevant information.POST /v2/contracts/call-read/<contract>/<function>- evaluate and return the result of calling a Clarity function.POST /v2/fees/transaction- evaluate a given transaction and return transaction fee estimation data.GET /v2/accounts/<address>- get the currentnoncerequired for creating transactions.
- The
- The endpoints implemented by
stacks-blockchain-apiprovide data that thestacks-nodecan't due to various constraints.- Typically this is either data that the
stacks-nodedoesn't persist, or data that it cannot efficiently serve to many clients. For example, thestacks-nodecan return the current STX balance of an account, but it can't return a history of account transactions. - The API also implements the Rosetta spec created by Coinbase -- "an open standard designed to simplify blockchain deployment and interaction."
- The API also implements the BNS (Blockchain Naming System) endpoints.
- See
/src/api/routesfor the Express.js routes.
- Typically this is either data that the
- The API creates an "event observer" http server which listens for events from a
stacks-node"event emitter"- These events are http POST requests that contain things like blocks, transactions, byproducts of executed transactions.
- Transaction "byproducts" are things like asset transfers, smart-contract log data, execution cost data.
- The API processes and stores these as relational data in postgres.
- See
/src/event-streamfor the "event observer" code.
- These events are http POST requests that contain things like blocks, transactions, byproducts of executed transactions.
- All http endpoints and responses are defined in OpenAPI and JSON Schema.
- See
/docs/openapi.yaml - These are used to auto generate the docs at https://hirosystems.github.io/stacks-blockchain-api/
- The JSON Schemas are converted into Typescript interfaces, which are used internally by the db controller module to transform SQL query results into the correct object shapes.
- ALSO the OpenAPI + JSONSchemas are used to generate a standalone
@stacks/blockchain-api-client.
- See
- The easiest/quickest way to develop in this repo is using the VS Code debugger. It uses docker-compose to setup a
stacks-nodeand Postgres instance.- Alternatively, you can run
npm run dev:integratedwhich does the same thing but without a debugger.
- Alternatively, you can run